前言
为什么要使用 mock?
Mock 可以理解为创建一个虚假的对象,或者说模拟出一个对象,在测试环境中用来替换掉真实的对象,以达到我们可以:
- 验证该对象的某些方法的调用情况,调用了多少次,参数是多少
- 给这个对象的行为做一个定义,来指定返回结果或者指定特定的动作
Junit5 + Mockito 整合
pom.xml 中引入下面的依赖
<!--注意: springboot版本为2.7.5-->
<!--mockito-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>4.5.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>5.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Mockito 中的常用方法
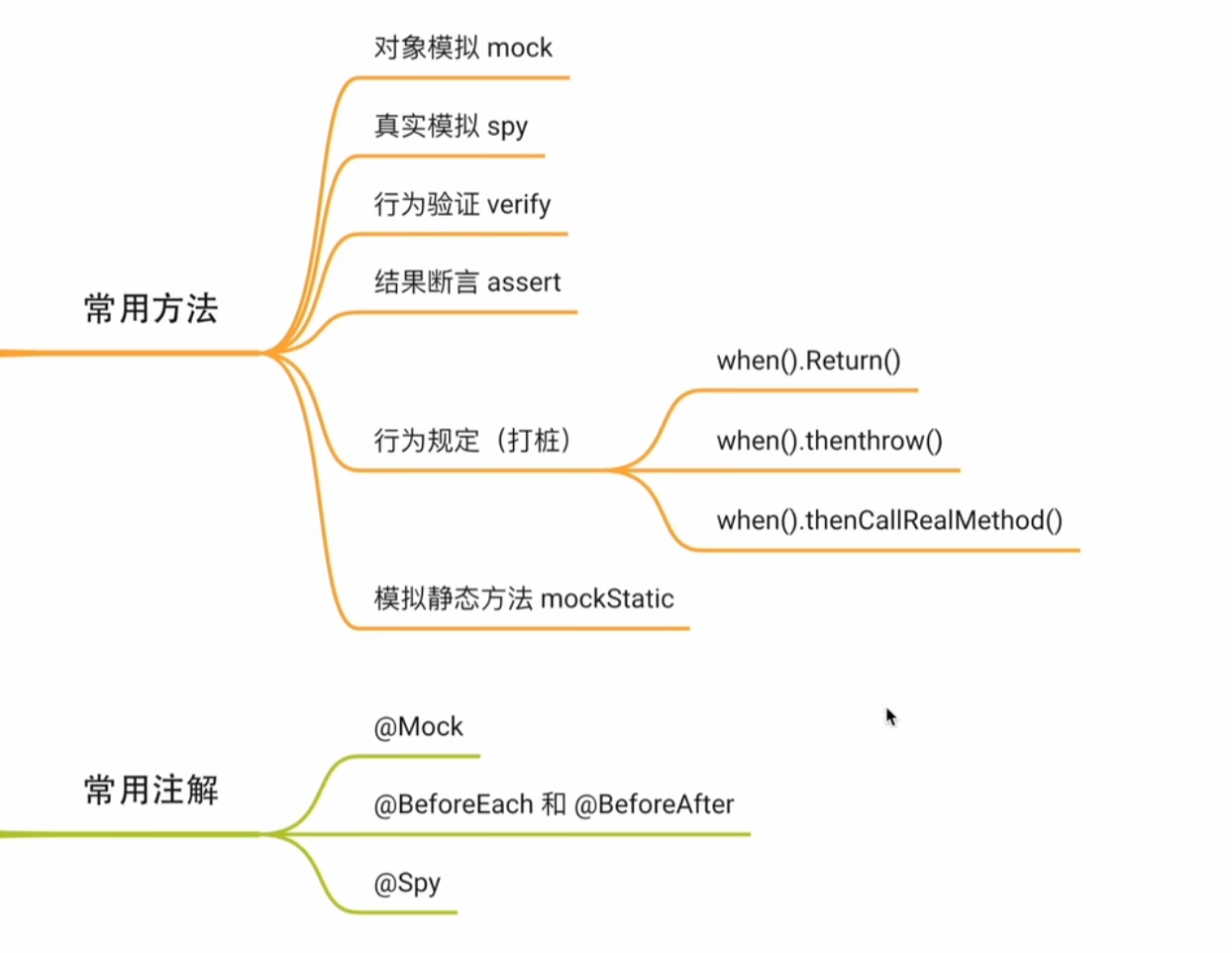
mock()与@Mock
mock() 方法来自 org.mockito.Mock,它表示可以 mock 一个对象或者是接口:
public static <T> T mock(Class<T> classToMock)
- classToMock:待 mock 对象的 class 类
- 返回 mock 出来的类
案例:
使用 mock() 方法 mock 一个类
Random random = Mockito.mock(Random.class);
以上等同于使用如下注解@Mock
@Mock
private Random random;
一般都使用注解的方式去 mock 类
对 Mock 出来的对象进行行为验证和结果断言
验证是校验待验证的对象是否发生过某些行为,Mockito 中验证的方法是:verify()
verify(mock).someMethod("some arg");
verify(mock, times(1)).someMethod("some arg");
使用 verify 验证:
verify 配合 time() 方法,可以校验某些操作发生的次数。
@Test
void check() {
Random random = Mockito.mock(Random.class, "test");
System.out.println(random.nextInt());
Mockito.verify(random,Mockito.times(2)).nextInt();
}
断言使用到的类是 Assertions.
Random random = Mockito.mock(Random.class, "test");
Assertions.assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());
输出结果:
org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError:
Expected :100
Actual :0
当使用 mock 对象时,如果不对其行为进行定义,则 mock 对象方法的返回值为返回类型的默认值。
给 Mock 对象打桩
打桩可以理解为 mock 对象规定一行的行为,使其按照我们的要求来执行具体的操作。
在 Mockito 中,常用的打桩方法为:
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
when().thenReturn() | Mock 对象在触发指定行为后返回指定值 |
when().thenThrow() | Mock 对象在触发指定行为后抛出指定异常 |
when().doCallRealMethod() | Mock 对象在触发指定行为后调用真实的方法 |
thenReturn() 代码示例
@Test
void check() {
Random random = Mockito.mock(Random.class, "test");
Mockito.when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100);
Assertions.assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());
}
测试通过
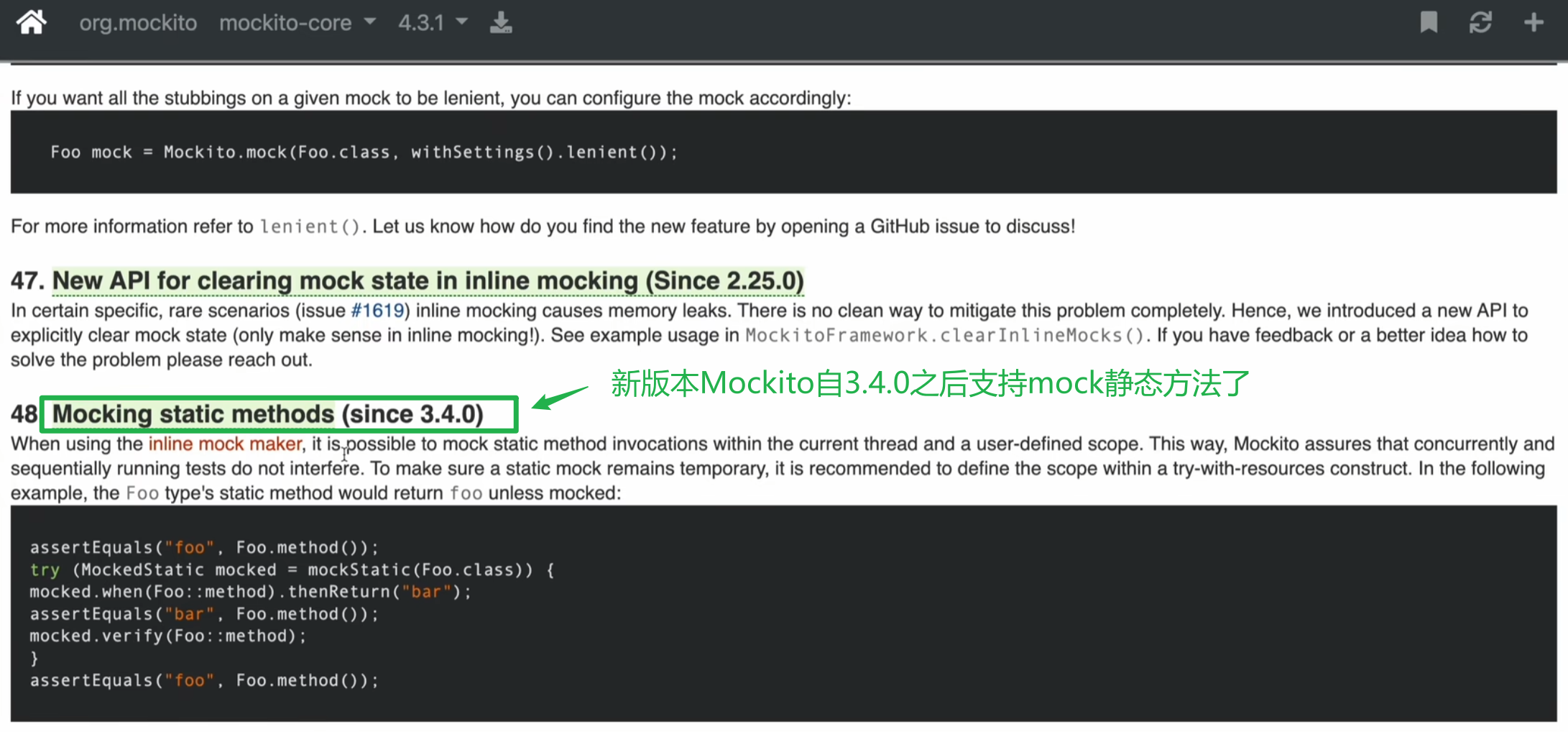
Mock 静态方法
新版本的 Mockito 是支持 mock 静态方法的,因此省去了再引入 PowerMock 的必要。
<!--注意: springboot版本为2.7.5-->
<!--注意: mockito 和 mockito-inline 不能同时引入-->
<!--mockito-->
<!--<dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version>4.5.1</version>-->
<!-- <scope>test</scope>-->
<!--</dependency>-->
<!--mockito-inline-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-inline</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
使用 mockStatic() 方法来 mock 静态方法的所属类,此方法返回一个具有作用域的模拟对象。
@Test
void range() {
MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities = Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class);
utilities.when(() -> StaticUtils.range(2, 6)).thenReturn(Arrays.asList(10, 11, 12));
Assertions.assertTrue(StaticUtils.range(2, 6).contains(10));
}
@Test
void name() {
MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities = Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class);
utilities.when(StaticUtils::name).thenReturn("bilibili");
Assertions.assertEquals("1", StaticUtils. name());
}
执行整个测试类后会报错:
org.mockito.exceptions.base.MockitoException:
For com.echo.mockito.Util.StaticUtils, static mocking is already registered in the current thread
To create a new mock, the existing static mock registration must be deregistered
原因是因为
mockStatic()方法是将当前需要 mock 的类注册到本地线程上(ThreadLocal),而这个注册在一次 mock 使用完之后是不会消失的,需要我们手动的去销毁。如过没有销毁,再次 mock 这个类的时候 Mockito 将会提示我们 :“当前对象 mock 的对象已经在线程中注册了,请先撤销注册后再试”。这样做的目的也是为了保证模拟出来的对象之间是相互隔离的,保证同时和连续的测试不会收到上下文的影响。
因此我们修改代码:
用try-with-resources去使用静态 mock 出来的类,每次使用完将资源释放。
class StaticUtilsTest {
@Test
void range() {
try (MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities = Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class)) {
utilities.when(() -> StaticUtils.range(2, 6)).thenReturn(Arrays.asList(10, 11, 12));
Assertions.assertTrue(StaticUtils.range(2, 6).contains(10));
}
}
@Test
void name() {
try (MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities = Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class)) {
utilities.when(StaticUtils::name).thenReturn("bilibili");
Assertions.assertEquals("bilibili", StaticUtils.name());
}
}
}
常用注解
可以代替
mock()方法的@Mock注解
如上所述,但需要注意的是:
@Mock 注解需要搭配 MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(testClass) 方法一起使用。
而我们往往会把开启注解支持这步放入@BeforeEach注解过的 setUp() 中:
package com.test.demo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;
import org.mockito.Spy;
import java.util.Random;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.*;
class DemoTest {
@Mock
private Random random;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
// 开启 Mock 注解
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@Test
void should_return_100_when_let_random_invoke_nextInt_by_mock() {
Mockito.when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100);
assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());
}
}
@BeforeEach与@BeforeAfter注解
Junit5 中,@Before 和 @After 注解被 @BeforeEach 和 @AfterEach 所替代,这是与 Junit4 的差异。
@Mock
private Random random;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
System.out.println("----测试开始----");
}
@Test
void check() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
Mockito.when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100);
Assertions.assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());
}
@AfterEach
void after() {
System.out.println("----测试结束----");
}
spy()方法与@Spy注解
- 被 spy 的对象会走真实的方法,而 mock 的对象不会
spy()的参数是对象实例,mock()的参数是 class- 被 spy 的对象会走真实的方法,而 mock 的对象不会
spy()的参数是对象实例,mock()的参数是 class
示例:spy 方法与 mock 方法的对比
@Test
void check() {
CheckAuthorityImpl checkAuthority = Mockito.spy(new CheckAuthorityImpl());
int res = checkAuthority.add(1, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals(3, res);
CheckAuthorityImpl checkAuthority1 = Mockito.mock(CheckAuthorityImpl.class);
int res1 = checkAuthority1.add(1, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals(3, res1);
}
输出结果:第二个 Assertions 断言失败,因为没有给 checkAuthority1 对象打桩,因此返回默认值
org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError:
Expected :3
Actual :0
同样的,我们往往也喜欢使用 @Spy 注解,代码示例:
@Spy
private CheckAuthorityImpl checkAuthority;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@Test
void check() {
int res = checkAuthority.add(1, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals(3, res);
}
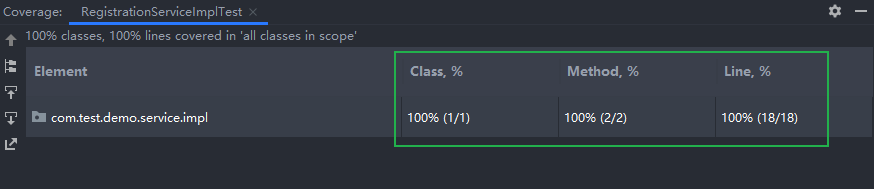
如何提升单测的代码覆盖率
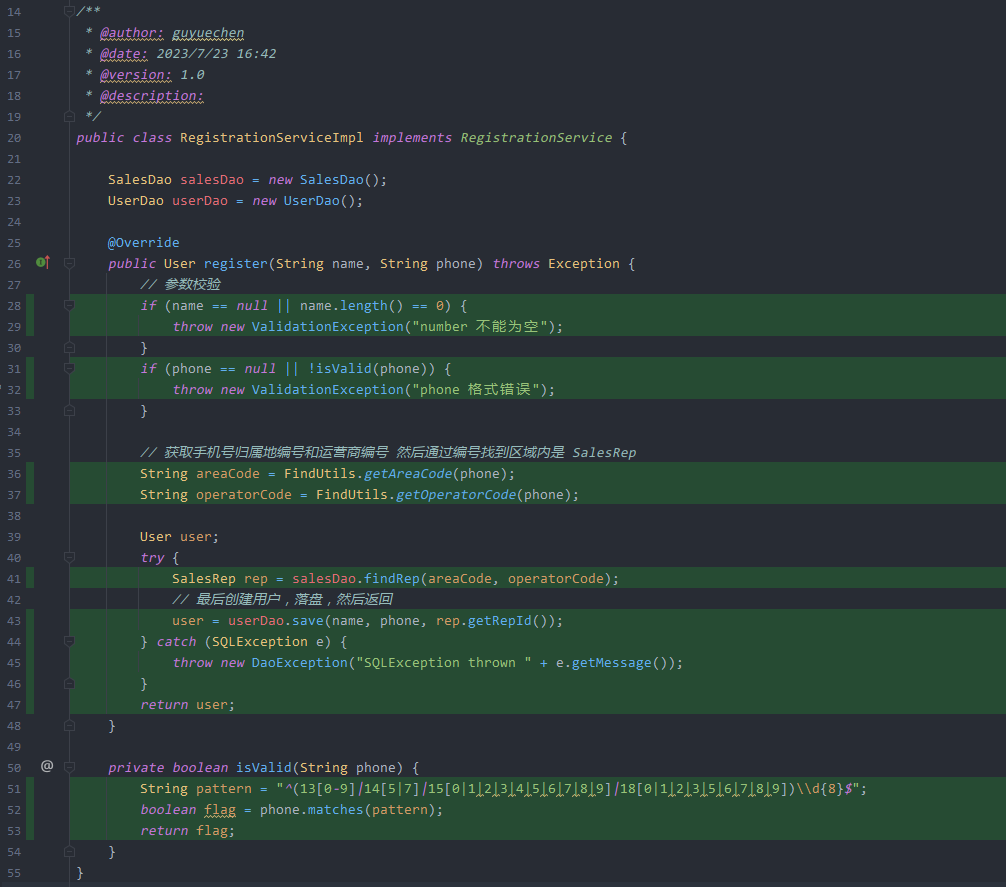
一个被测类如下
package com.test.demo.service.impl;
import com.test.demo.dao.SalesDao;
import com.test.demo.dao.UserDao;
import com.test.demo.entity.SalesRep;
import com.test.demo.entity.User;
import com.test.demo.exception.DaoException;
import com.test.demo.exception.ValidationException;
import com.test.demo.service.RegistrationService;
import com.test.demo.util.FindUtils;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* @author: guyuechen
* @date: 2023/7/23 16:42
* @version: 1.0
* @description:
*/
public class RegistrationServiceImpl implements RegistrationService {
SalesDao salesDao = new SalesDao();
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
@Override
public User register(String name, String phone) throws Exception {
// 参数校验
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
throw new ValidationException("number 不能为空");
}
if (phone == null || !isValid(phone)) {
throw new ValidationException("phone 格式错误");
}
// 获取手机号归属地编号和运营商编号 然后通过编号找到区域内是 SalesRep
String areaCode = FindUtils.getAreaCode(phone);
String operatorCode = FindUtils.getOperatorCode(phone);
User user;
try {
SalesRep rep = salesDao.findRep(areaCode, operatorCode);
// 最后创建用户,落盘,然后返回
user = userDao.save(name, phone, rep.getRepId());
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new DaoException("SQLException thrown " + e.getMessage());
}
return user;
}
private boolean isValid(String phone) {
String pattern = "^(13[0-9]|14[5|7]|15[0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9]|18[0|1|2|3|5|6|7|8|9])\\d{8}$";
boolean flag = phone.matches(pattern);
return flag;
}
}
观察测试类中是如何覆盖被测类中的所有代码的:
package com.test.demo.service.impl;
import com.test.demo.dao.SalesDao;
import com.test.demo.dao.UserDao;
import com.test.demo.entity.User;
import com.test.demo.exception.DaoException;
import com.test.demo.exception.ValidationException;
import com.test.demo.util.FindUtils;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.mockito.*;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.*;
class RegistrationServiceImplTest {
@InjectMocks
@Spy
private RegistrationServiceImpl registrationService;
@Mock
private SalesDao salesDao;
@Mock
private UserDao userDao;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
}
@Test
void should_throw_ValidationException_when_register_invalid_inputs() {
// name 为空的情况
String name = null;
String phone = "18101971080";
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
} catch (Exception e) {
assertTrue(e instanceof ValidationException);
}
// phone 为空的情况
name = "大话西游";
phone = null;
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
} catch (Exception e) {
assertTrue(e instanceof ValidationException);
}
}
@Test
void should_throw_DaoException_when_register_wrong_phone() throws SQLException {
String name = "大话西游";
String phone = "18101971080";
try (MockedStatic<FindUtils> findUtils = mockStatic(FindUtils.class)) {
// 给静态方法打桩
findUtils.when(() -> FindUtils.getAreaCode(phone)).thenReturn("a");
findUtils.when(() -> FindUtils.getOperatorCode(phone)).thenReturn("b");
// 数据库 userDao 异常的情况
when(salesDao.findRep("a", "b")).thenCallRealMethod();
when(userDao.save(name, phone, "SUCCESS0001")).thenThrow(new SQLException()); // 异常打桩
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
} catch (Exception e) {
assertTrue(e instanceof DaoException);
}
}
}
@Test
void should_return_user_when_register() throws Exception {
String name = "大话西游";
String phone = "18101971080";
try (MockedStatic<FindUtils> findUtils = mockStatic(FindUtils.class)) {
// 给静态方法打桩
findUtils.when(() -> FindUtils.getAreaCode("18101971080")).thenReturn("a");
findUtils.when(() -> FindUtils.getOperatorCode("18101971080")).thenReturn("b");
// 数据库正常的情况
when(salesDao.findRep("a", "b")).thenCallRealMethod();
when(userDao.save(name, phone, "SUCCESS0001")).thenCallRealMethod();
User user = registrationService.register(name, phone);
assertEquals("SUCCESS0001", user.getRepId());
}
}
}
上述测试的结果